Gastroshiza is a medical condition that, while not widely known, can significantly impact a person’s digestive health and overall well-being. For many, encountering unfamiliar terms like this can be intimidating, but understanding the condition, its causes, and how to manage it is the first step toward maintaining a healthy digestive system. This article provides a clear, practical guide to Gastroshiza, covering everything from identification and diagnosis to treatment options and preventive measures.
Understanding Gastroshiza
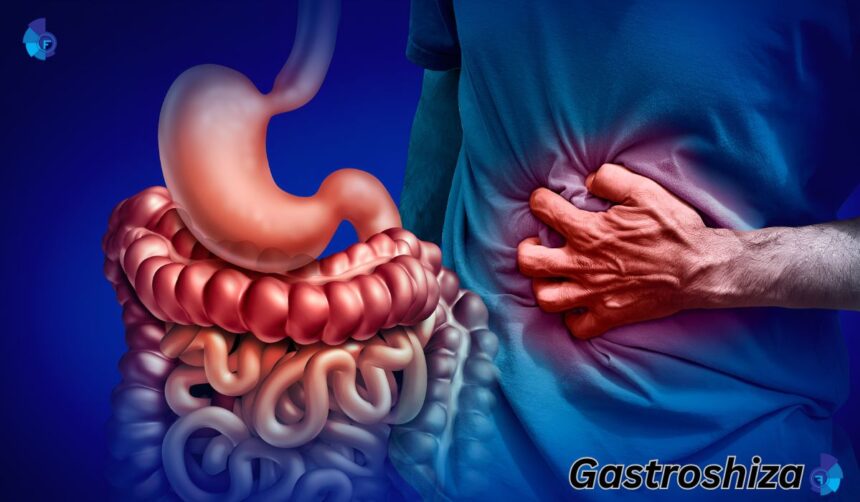
Gastroshiza is a condition that primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract, causing a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity and frequency. At its core, the condition is linked to disruptions in the normal digestive processes, often leading to discomfort, irregular bowel habits, and other related health challenges. While the exact cause is still being studied, medical professionals believe that a combination of lifestyle factors, genetics, and environmental influences can contribute to its development.
Recognizing the signs of Gastroshiza early can make a substantial difference in outcomes. The condition may manifest differently depending on age, overall health, and existing medical conditions. Because the symptoms can sometimes resemble those of more common digestive issues, accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Common Symptoms of Gastroshiza
People with Gastroshiza often experience a mix of gastrointestinal disturbances. Some of the most common symptoms include persistent abdominal discomfort, bloating, and irregular bowel movements. Individuals may also report sudden episodes of nausea or changes in appetite. While these symptoms might seem mild at first, they can gradually interfere with daily activities if left unaddressed.
In addition to digestive discomfort, some individuals notice fatigue or a general feeling of malaise. This is often linked to the body’s reduced ability to absorb nutrients effectively. Understanding the full spectrum of symptoms can help in identifying the condition sooner and seeking appropriate medical care.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of Gastroshiza is influenced by multiple factors. Diet and lifestyle play a significant role; diets high in processed foods, excessive sugar, and low fiber content can contribute to the condition. Stress and lack of regular physical activity are also known to affect digestive health, potentially triggering or exacerbating symptoms.
Genetics can be another factor. Individuals with a family history of gastrointestinal disorders may be more susceptible to developing Gastroshiza. Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain toxins or pathogens, might also contribute. Understanding these risk factors allows individuals to make informed lifestyle changes to minimize the likelihood of developing the condition.
How Gastroshiza Is Diagnosed
Accurate diagnosis of Gastroshiza involves a combination of clinical evaluation, symptom analysis, and medical testing. Physicians typically begin with a detailed discussion of the patient’s medical history and a review of current symptoms. This helps in distinguishing Gastroshiza from other digestive disorders with similar presentations.
Medical tests may include blood work, imaging studies, and stool analysis to assess digestive function and rule out infections or other conditions. In some cases, endoscopic procedures are necessary to examine the gastrointestinal tract more closely. A comprehensive approach ensures that the diagnosis is precise, paving the way for targeted treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Gastroshiza
Managing Gastroshiza effectively often requires a combination of medical intervention, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes. Doctors may recommend specific medications to relieve symptoms, improve digestive function, or address underlying causes. These treatments are usually personalized to suit the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
Dietary adjustments play a crucial role in treatment. Incorporating high-fiber foods, reducing processed and fatty foods, and maintaining proper hydration can significantly improve digestive health. Additionally, introducing probiotics may support a balanced gut microbiome, helping to alleviate symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Digestive Health
Lifestyle modifications can complement medical treatments and improve long-term outcomes. Regular physical activity stimulates digestion and reduces stress, both of which are beneficial for managing Gastroshiza. Adequate sleep and mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, can also help regulate digestive function.
Avoiding triggers is another key strategy. This may include limiting alcohol consumption, reducing caffeine intake, and being mindful of foods that commonly cause bloating or discomfort. By adopting these healthy habits, individuals can support their digestive system and reduce the risk of symptom recurrence.
The Role of Nutrition in Managing Gastroshiza
Nutrition is a cornerstone of managing Gastroshiza. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support the digestive system. Fiber, in particular, helps regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation, a common issue for those with Gastroshiza.
It is equally important to monitor food sensitivities. Some individuals may experience worsened symptoms after consuming dairy, gluten, or high-fat foods. Keeping a food diary and tracking symptoms can help identify personal triggers, enabling more precise dietary adjustments for long-term relief.
Preventing Gastroshiza
Prevention of Gastroshiza is closely tied to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and attentive dietary habits. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help detect early signs of digestive distress, allowing for timely interventions. Proactive measures, such as managing stress, staying physically active, and following a nutrient-rich diet, play a significant role in reducing the risk of developing the condition.
Hydration is another essential preventive measure. Drinking adequate water daily aids digestion, supports nutrient absorption, and helps prevent constipation. Small lifestyle choices, when consistently applied, can make a significant difference in long-term digestive health.
Coping Strategies for Daily Life
Living with Gastroshiza can be challenging, but practical strategies can make day-to-day life more manageable. Planning meals ahead, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a routine for physical activity are effective ways to manage symptoms. Mindful eating practices, such as eating slowly and chewing thoroughly, can also reduce digestive discomfort.
Support networks, whether through friends, family, or healthcare communities, can provide emotional support and practical advice. Understanding that Gastroshiza is manageable with the right approach can empower individuals to take control of their health and maintain a high quality of life.
Long-Term Outlook
With appropriate management, the long-term outlook for individuals with Gastroshiza is generally positive. Most people respond well to a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical treatment. While flare-ups may occur, they are often preventable through proactive habits and attentive care.
Ongoing monitoring and regular medical consultations help ensure that the condition remains under control. Adopting a proactive approach to digestive health can prevent complications and improve overall well-being, allowing individuals to lead active, fulfilling lives despite the condition.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is essential to seek professional guidance if symptoms worsen or persist despite self-care measures. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes. Signs that indicate the need for medical evaluation include severe abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, persistent vomiting, or changes in bowel habits that last more than a few days.
Healthcare providers can provide tailored advice, recommend diagnostic tests, and develop a treatment plan suited to the individual’s needs. Timely medical attention ensures that Gastroshiza is managed effectively and reduces the likelihood of long-term complications.
Final Thoughts
Gastroshiza may not be widely recognized, but it is a condition that warrants attention due to its potential impact on digestive health and overall quality of life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive strategies is crucial for anyone who suspects they might be affected or is looking to maintain a healthy digestive system. Through proper diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, and dietary adjustments, individuals can manage Gastroshiza successfully and reduce the likelihood of recurring issues. Awareness and proactive care are key to living comfortably with this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Gastroshiza and who can get it?
Gastroshiza is a digestive condition affecting the gastrointestinal tract, often causing abdominal discomfort, irregular bowel movements, and other digestive issues. It can occur in anyone, though lifestyle factors, genetics, and stress may increase susceptibility.
2. What are the early signs of Gastroshiza?
Early signs include bloating, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and occasional nausea. Recognizing these signs early helps in seeking timely medical care and preventing worsening symptoms.
3. How is Gastroshiza diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a combination of medical history review, symptom evaluation, and tests such as blood work, stool analysis, or imaging studies. Sometimes endoscopy is used to examine the gastrointestinal tract in detail.
4. Can diet changes help manage Gastroshiza?
Yes, diet plays a major role. Eating high-fiber foods, staying hydrated, avoiding processed and high-fat foods, and monitoring food sensitivities can significantly improve symptoms and overall digestive health.
5. Are there medications for Gastroshiza?
Depending on severity, doctors may prescribe medications to relieve symptoms or treat underlying causes. This is often combined with lifestyle adjustments for the best results.
6. Is Gastroshiza preventable?
While not all cases are preventable, maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, managing stress, and regular medical check-ups can greatly reduce the risk of developing the condition.
7. Can lifestyle changes improve long-term outcomes?
Absolutely. Consistent exercise, proper sleep, mindful eating, and avoiding triggers like alcohol and caffeine can support digestive health and minimize flare-ups over time.
For More: fogmagazine.co.uk